DM WebSoft LLP exceeded our expectations! Their seasoned team of experts delivered a website that perfectly captures our brand essence. Their 15+ years of experience truly shine through in their exceptional web development skills.
How to Build Accessible Web Applications with React

TABLE OF CONTENT
Get in Touch
Introduction

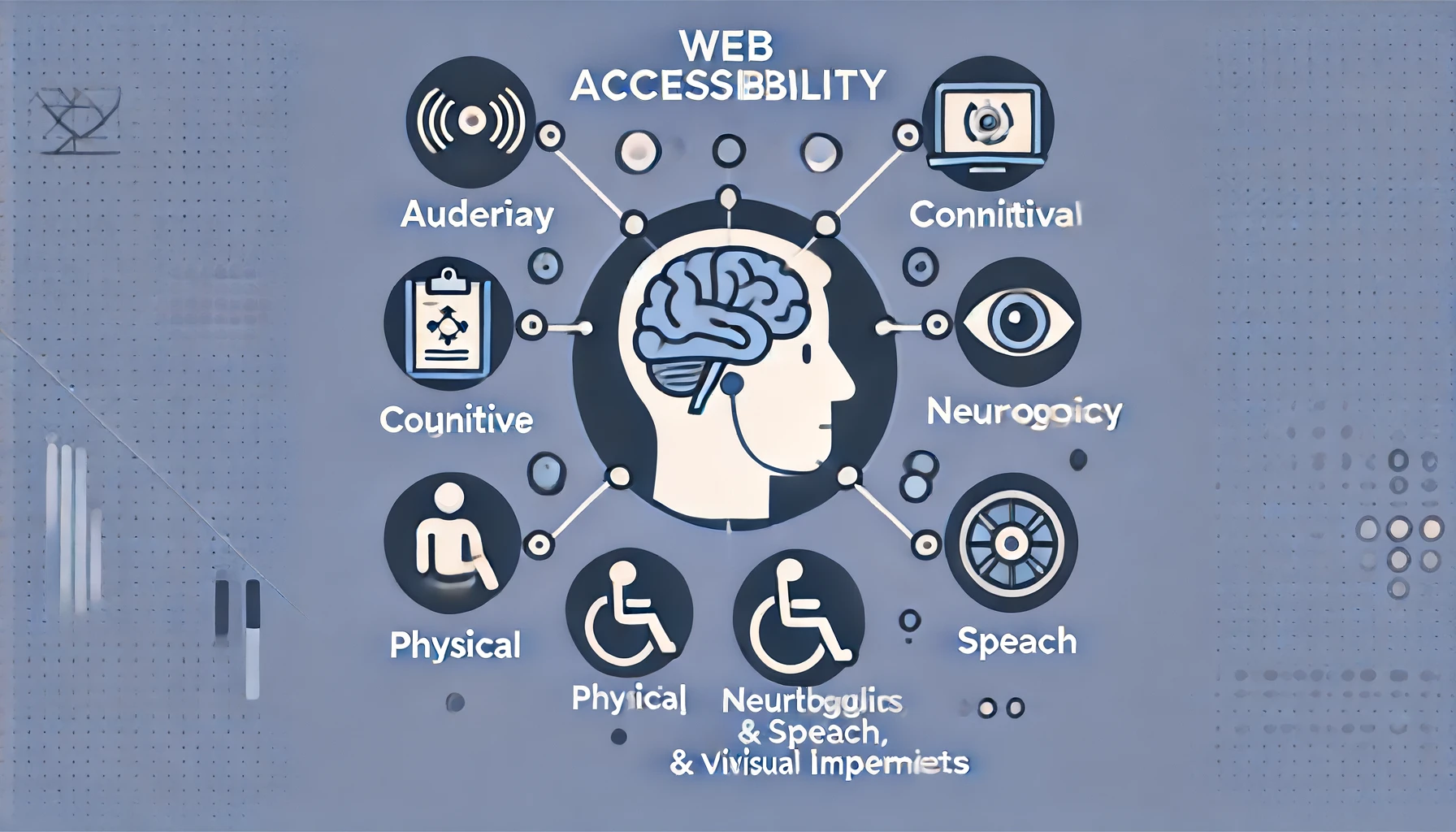
Web applications developed today must be accessible to all users in the digital environment. Web accessibility is not only a legal requirement but also an important principle of design. It ensures that people with disabilities will have equally meaningful interactions with web content, including people who are auditory, cognitive, neurological, physical, speech, and visually impaired. Using the priority of access helps us create a better internet for all.
At DM WebSoft LLP, we understand the serious business of creating web applications that are accessible to all. Our commitment to accessibility stands with every project we handle. We have superior potential with React to help companies develop web applications that are not just functional but user-friendly; this is in line with most accessibility standards, which include the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines and the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Web accessibility ensures that web content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust. These are the POUR principles, which guarantee that web applications can be used efficiently by any kind of user, regardless of ability. For example, providing a text alternative for non-text content benefits users with screen readers. At the same time, ensuring keyboard accessibility benefits those who cannot use a mouse to interact with the site.
The best and most efficient strategy is to develop inclusive web applications while implementing accessibility from the beginning of the project. Some practices include using semantic HTML, roles from ARIA, proper keyboard navigation, etc. By this, we not only meet legal standards but also improve the user experience on the whole, making our web application much more attractive and easy to use.
We can, therefore, develop accessible and high-performance web applications using our experience with React. We fix identified issues in the development stage with tools like react-axe and eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y. We also do detailed manual testing using screen readers to ensure our applications are fully accessible.
Accessibility at DM WebSoft LLP is an ongoing activity. Regular testing and updating must, therefore, be done to ensure that changes in technology do not erode accessibility. This is how we provide our web applications adhere to the best practices for total inclusivity and are made compatible with users.
Further, in this blog post, we’ll dig into details—common issues and practical steps toward building accessible web applications with React—to understand more about the importance of web accessibility.
Understanding Web Accessibility
Need for Accessibility in Web Development
General Inaccessible Web Applications
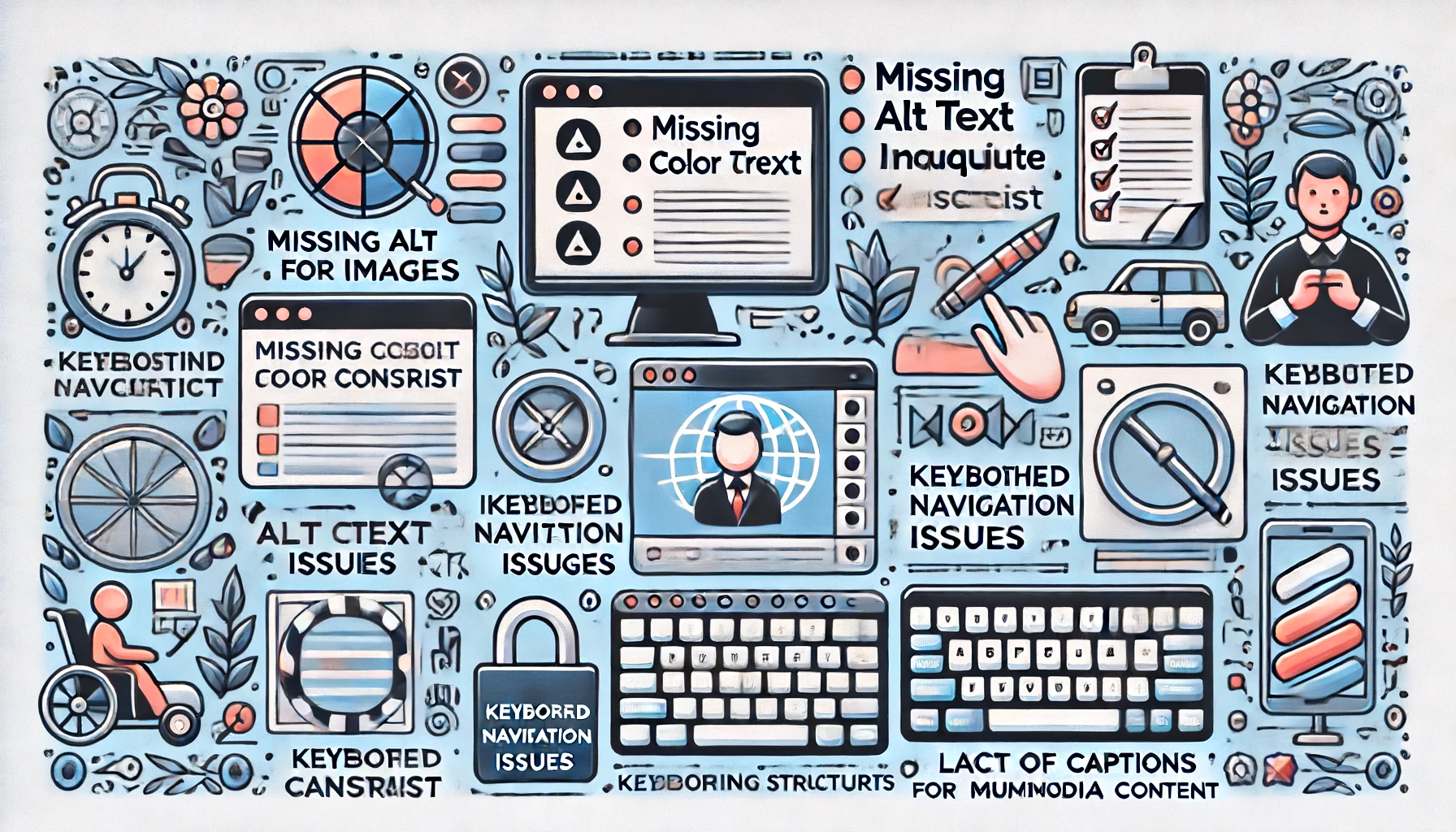
Information about creating accessible web apps is important to make sure all users have the chance to view and interact with your content. With that said, there are a few common issues that can be challenges to access. With an understanding of these problems, you’ll be on your way to creating a more inclusive web experience.
Missing Alt Text for Images
Alt text describes an image that screen readers use, as visually impaired users depend on screen readers. Without alt text on the photos, such users will miss out on content. For instance, a product image on an e-commerce site lacks alt text.
Solution: Make sure all photos have meaningful alt text that accurately describes the content or function of the image. In decorative images, assign the empty alt attribute (alt=””) to let the screen reader know that this image is for decoration only and its content does not matter for the user’s content.
Insufficient Color Contrast
The color contrast is based on how bright or dark the text color is compared to its background color. Text can be made unreadable for some users if there is insufficient color contrast between text and background colors. For instance, the text written in gray on a white background won’t be readable.
Solution: The colors need to contrast against each other enough so that they can easily be read. Tools like WebAIM’s Contrast Checker can help you figure out whether your choice of colors have good contrast ratio against each other or not. A suggested minimum: 4.5:1 for regular text and 3:1 for large text.
Keyboard Navigation Deficiencies
An alternative to navigating web applications is keyboard navigation. An interaction made possible with a typical user, one who is disabled and uses the keyboard instead of the mouse for such interactivity. Unless they can reach all interactive elements, like buttons, links, or form fields, using a keyboard, they are stuck. Typical examples are missing focus indicators and traps: the keyboard focus gets stuck.
Solution: Make all interactive elements available via keyboard. Use proper HTML elements and attributes for the focus states, and ensure that focus indicators have sufficient contrast to be seen and can be clearly distinguished to which element they apply. You can simulate this by testing your web application using only the keyboard.
Incorrect Heading Levels
Headings provide a way to organize the content on a page so that it can be browsed or read. Some of these incorrectly or poorly done missing heading structures are a huge nightmare to the user, especially with assistive technologies like screen readers that rely on the number of headings to navigate content.
Solution: Use headings tags, <h1> through <h6>, which lead to a logical structure in building the content. For every page, use one <h1> tag for the main heading, then continue implementing <h2> tags for subheadings, and so forth. And there, you get not just a good opportunity for better accessibility but also great SEO.
Multimedia content not provided with captions or transcripts separates deaf and hard-of-hearing users. Captions/transcripts offer an equivalent alternative to auditory information for the content so that users without hearing have access.
Solution: Captions for all video content and transcripts for all other audio content. Tools and services are available to help you generate accurate captions and transcripts, ensuring that all users can access your multimedia content (WebAIM) (Semrush).
Real-Life Success Stories of Accessibility Barriers
Example 1: A popular news website lacked alt text for images in its articles, making it difficult for screen reader users to understand the context of the images. An example of such a case is an online learning platform that uses low-contrast text colors; it will be difficult for students with visual impairments to read the content. On an e-commerce site, buttons had been designed in a way that blocked users from being able to access them via keyboard to complete a transaction. These issues are just some of those that need fixing, and they greatly bar common accessibilities. This not only helps in achieving the standard of access but also adds to general usability and all-encompassing aspects of your web application.
We are experts at DM WebSoft LLP in identifying and debugging these frequent issues that arise due to accessibility. Our experience with React and the accessibility standards guarantees that us to deliver web applications that are inclusive and easy to use. Contact us today to find out more about how we can help build your organization a web application that is accessible and meets the needs of all users.
Building Accessible Web Applications with React

Designing and developing accessible web applications include several processes: the right tool, following best practices, and understanding the user’s needs who live with a disability. React is one of the most popular JavaScript libraries used in building user interfaces. It provides several features and techniques that ensure a web application is accessible. In the following section, we outline how to make React applications more accessible.
Writing Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML involves the use of HTML elements that have meaning innately described well, since, through this, it’s easy for screen readers and assistive technologies to understand and navigate your content easily.
Examples of Semantic HTML:
- The structure of your page should be established using <header>, <main>, <footer>, and <nav>.
- You can separate the content of the page into sections that are easy to handle by defining them using <article> and <section>.
- Use <button> where the elements a user will interact with to trigger actions will need wrapping.
- For semantic HTML, you give a clear structure that is more accessible and performs better for SEO.
Implementing ARIA Roles and Properties
ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles and properties enhance the accessibility of web applications, more so with custom components that do not use native HTML elements. ARIA attributes provide extra information to assistive technologies about the roles, states, and properties of elements.
Familiar ARIA Attributes:
- role: Defines the role of an element. For example, role=”button” may be used for a custom button.
- aria-label: Gives the name of a component.
- aria-labelledby: Identifies the aspect that is labeled by the current element.
- aria-live: Marks an element so users can identify when its contents are updated.
Example:
<span aria-hidden=”true”>×</span>
</button>
By using ARIA attributes, you could give access to custom components.
Making Sure Keyboard Navigation is Accessible
Making sure that everything interactive on a website can be navigated through a keyboard is essential. This means how to handle focus states and having visible focus indicators.
Best Practices:
- Use tabindex attributes to manage the elements’ tab order.
- Add event handlers for focus and blur events to manage the focus state.
- Make sure all interactive elements can be navigated using a keyboard.
Example:
Click me
</button>
Testing your web application with just a keyboard helps identify and fix navigation issues.
Focus Management
Focus management is the practice of making it possible for users to get through interactive elements with a keyboard, which implies having vital visual feedback for which element currently has focus.
Example:
<button style={{ outline: ‘2px solid blue’ }}>
Custom Button
</button>
);
By managing the focus states well, you make your app even more navigable and usable for those very few end users who use a keyboard to navigate your application.
Leverage React Accessibility Tooling
React has great tooling that helps developers create accessible web applications. These tools can catch all sorts of accessibility concerns and provide developers with actionable feedback.
Popular Tools:
- react-axe: An accessibility auditing tool for React apps.
- eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y: A linting plugin that helps you enforce accessibility rules on JSX.
Example:
import axe from “react-axe”;
import { render } from “react-dom”;
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’) {
axe(React, ReactDOM, 1000);
}
render(<App />, document.getElementById(‘root’));
The above tools add proper measures for not only detecting accessibility issues but also help improve human-human interactions.
We build accessible web apps using React at DM WebSoft LLP. We create applications that not only perform well but also remain functional and meet accessibility standards. Reach out to us for building inclusive and user-friendly web applications.
Tools and Resources for Ensuring Accessibility in React Applications

Ensure accessibility in React applications by using tools and resources to meet the standards. These tools help to identify and fix accessibility issues when designing web applications using React; as a result, the applications become inclusive and usable for all users. Below are some tools and resources that one should consider when aiming to ensure the highest level of accessibility in a particular application developed in React.
Linting tools
eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y: A plugin for ESLint that lints accessibility in your JavaScript source. It raises cautions and typical pain point errors of accessibility, helping developers catch many problems earlier in the development process.
Example:
module.exports = {
plugins: [
‘jsx-a11y’,
],
rules: {
‘jsx-a11y/anchor-is-valid’: ‘warn’,
‘jsx-a11y/alt-text’: ‘warn’,
‘jsx-a11y/no-static-element-interactions’: ‘warn’,
// Add other rules as needed
},
};
By adding eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y to your workflow you can ensure you are following all best practices for writing accessible React code. It integrates with your React development workflow, making it easy to identify and address accessibility problems as you code.
Example:
import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom’;
import axe from ‘react-axe’;
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’) {
axe(React, ReactDOM, 1000);
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById(‘root’));
This allows you to catch accessibility issues early, making your application accessible from the get-go.
Manual Testing Strategies
While automated tools are essential, manual testing ensures well-rounded accessibility coverage. Here are some manual testing strategies:
- Screen Readers: Test your application with screen readers such as NVDA (Windows) or VoiceOver (Mac) to help ensure that visually impaired users can easily consume the content.
- Keyboard Navigation: Walk around your application using only the keyboard. Check all interactive elements to ensure that they work and that focus is noticed on these elements so issues with this can be identified.
- Tools like WebAIM Contrast Checker: will be able to demonstrate or highlight whether the colors you have chosen in the design of your app are accessible; this way, you find out what things automated tools might miss. Manual testing will hence ensure you get a complete picture of application accessibility.
WCAG Guidelines
WCAG, or Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, are an extensive series of recommendations to make web content more accessible. WCAG is internationally recognized as a standard for web accessibility, ensuring three conformance levels: A, AA, and AAA.
- Level A: Basic web accessibility features.
- Level AA: Overcoming the most significant and most common barriers for disabled users.
- Level AAA: The highest and most complex level of web accessibility.
Ensuring that your web applications meet the standards set by WCAG guidelines guarantees they are at the legal and best practice standards for accessibility.
Additional Resources
- W3C WAI (Web Accessibility Initiative): Provides a wide range of resources, including guidelines, tutorials, and techniques concerning web accessibility.
- WebAIM (Web Accessibility In Mind): Publishes articles and creates tools and resources to improve your understanding of and abilities in making the web accessible.
- Accessibility Insights: These are the suite tools Microsoft offers to help developers identify and fix accessibility issues. With tooling like that, you can be sure that applications you will build with React are accessible, compliant, and good enough to ensure excellent user experience for all users.
DM WebSoft LLP: Where we use the above-mentioned suite of tools and resources to create Accessible Web Applications that meet the highest accessibility standards. Our React experts have collaborated with the accessibility team to ensure that solutions are constantly built inclusively, empathetically, and legally compliant. Write to us now to create accessible web applications that cater effectively to all users.
Conclusion

Creating accessible web applications is more than compliance; it’s about the ethical responsibility to ensure users, regardless of ability, can access and benefit from the contents. It is in this very blog that we discuss the importance of web accessibility, common pitfalls, and the practical steps you need to take to make your web applications accessible using React.
This means web accessibility is about making content perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust to users with disabilities. Using semantic HTML, implementing ARIA roles, and ensuring good keyboard navigation helps a lot in enhancing user experience for your web applications. It also maintains high levels of accessibility by using tools like react-axe, eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y, and WCAG guidelines.
We at DM WebSoft LLP commit ourselves to creating web applications that are totally user-friendly and comply with accessibility standards. With the knowledge and experience in React and dedication to accessibility, we will craft solutions for users that guarantee an impressive user experience.
Web accessibility ensures that websites are usable by people with disabilities.
It promotes inclusivity, enhances user experience, and complies with legal standards.
Tools like eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y and react-axe assist in ensuring accessibility.
Add descriptive alt text to all images.
ARIA roles provide additional context to screen readers for custom components.
Get Started Now !
What’s the Process ?
Request a Call
Consultation Meeting
Crafting a Tailored Proposal
Get Started Now !
Real Stories, Real Results. Discover What Our Clients Say

Working with DM WebSoft LLP was a game-changer for our business. Their technical prowess and innovative solutions transformed our online presence. A highly recommended web development agency with a stellar track record.

We are thrilled with the results DM WebSoft LLP delivered. Their deep understanding of web development coupled with years of expertise ensured a seamless and visually stunning website. True professionals!

In a digital age where first impressions matter, DM WebSoft LLP crafted a website that speaks volumes. The team’s attention to detail and commitment to quality set them apart. Thank you for making our vision a reality.

DM WebSoft LLP’s team demonstrated unparalleled expertise. Their ability to navigate complex technical challenges with ease is truly commendable. Choosing them for our web development needs was the best decision.

Exceptional service, unmatched skills! DM WebSoft LLP stands out as a leading web development agency. Their collaborative approach and commitment to excellence make them our go-to partner for all things web-related.

DM WebSoft LLP turned our ideas into a digital masterpiece. The seamless communication and timely delivery of our project showcased their professionalism. Highly impressed with the level of creativity and skill.

Our experience with DM WebSoft LLP was nothing short of amazing. From concept to execution, their team provided top-notch web development services. A reliable partner for businesses looking to elevate their online presence.

DM WebSoft LLP’s team of tech experts is second to none. Their wealth of experience reflects in the quality of their work. Our website not only meets but exceeds industry standards, thanks to their dedication.

Choosing DM WebSoft LLP was the best investment for our web development needs. Their team’s proficiency, coupled with a customer-centric approach, made the entire process smooth and enjoyable. A pleasure to work with!